The Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC)
Session Objectives
SDLC
7 Different SDLC Models
Recall the SDLC covered in the previous programming module. The SDLC is a process or framework which defines a set of procedures and tasks providing guidance for the developers and project managers involved in a project.
SDLC is a process followed for a software project, within a software organization.
It consists of a detailed plan describing how to develop, maintain, replace, and alter or enhance specific software.
The life cycle defines a methodology for improving the quality of software and the overall development
process.
SDLC Models
7 SDLC Models
Waterfall (Classical)
V-Shaped Model
Iterative
Spiral
Big Bang Model
Agile
RAD
SDLC Model – Waterfall
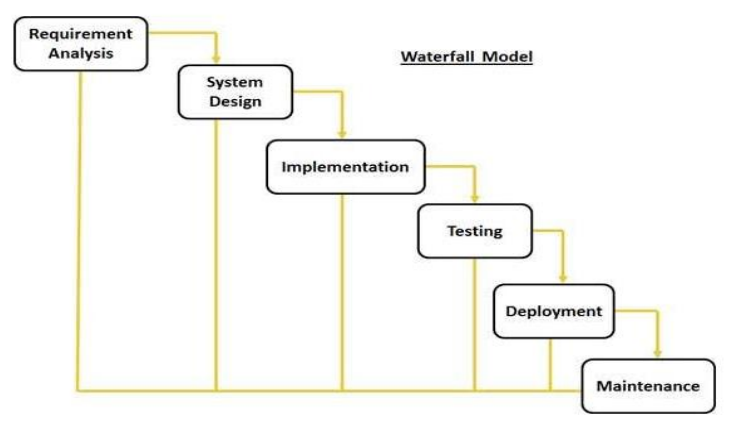
Requirement Gathering and analysis: All possible requirements of the system to be developed are captured in this phase and documented in a requirement specification doc.
System Design: The requirement specifications from first phase are studied in this phase and system design is prepared. System Design helps in specifying hardware and system requirements and also helps in defining overall system architecture.
Implementation: With inputs from system design, the system is first developed in small programs called units, which are integrated in the next phase. Each unit is developed and tested for its functionality which is referred to as Unit Testing.
Integration and Testing: All the units developed in the implementation phase are integrated into a system after testing of each unit. Post integration the entire system is tested for any faults and failures.
Deployment of system: Once the functional and non-functional testing is done, the product is deployed in the customer environment or released into the market.
Maintenance: There are some issues which come up in the client environment. To fix those issues patches are released. Also to enhance the product some better versions are released. Maintenance is done to deliver these changes in the customer environment.
SDLC V-Model
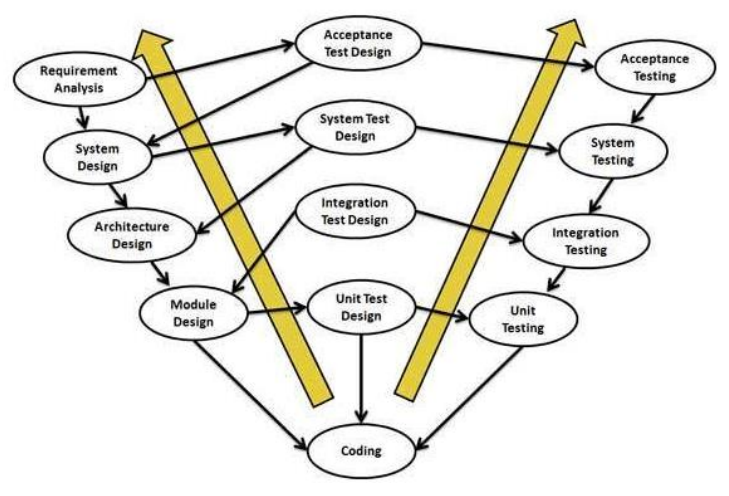
V- model means Verification and Validation model.
Just like the waterfall model, the V-Shaped life cycle is a sequential path of execution of processes.
Each phase must be completed before the next phase begins.
Testing of the product is planned in parallel with a corresponding phase of development in V-model.
SDLC Iterative
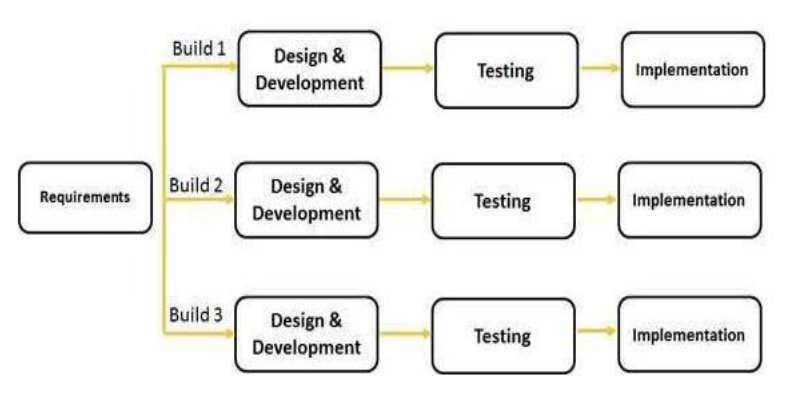
Iterative process starts with a simple implementation of a subset of the software requirements and
iteratively enhances the evolving versions until the full system is implemented.At each iteration, design modifications are made and new functional capabilities are added.
The basic idea behind this method is to develop a system through repeated cycles (iterative) and in smaller portions at a time (incremental).
SDLC Spiral
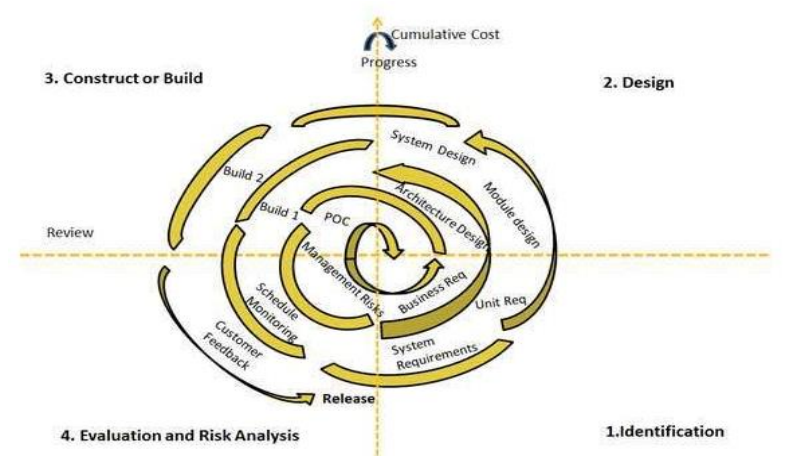
The spiral model has four phases.
A software project repeatedly passes through these phases in iterations called Spirals.
Identification
Design
Construct or Build
Evaluation and Risk analysis
1. Identification:
Gathering the business requirements in the baseline spiral.
In the subsequent spirals as the product matures, identification of system requirements, subsystem requirements and unit requirements are all done in this phase.
Requires continuous communication between the customer and the system analyst.
At the end of the spiral the product is deployed in the identified market.
2. Design
Starts with the conceptual design in the baseline spiral and involves
architectural design, logical design of modules, physical product
design and final design in the subsequent spirals.
3. Construct or Build
Production of the actual software product at every spiral.
In the baseline spiral when the product is just thought of and the design
is being developed a POC is developed in this phase to get customer
feedback.subsequent spirals with higher clarity on requirements and design
details a working model of the software called build is produced with a
version number.
4. Evaluation and Risk Analysis
Identifying, estimating, and monitoring technical feasibility and management risks, such as schedule slippage and cost overrun.
After testing the build, at the end of first iteration, the customer evaluates the software and provides feedback.
SDLC Big Bang
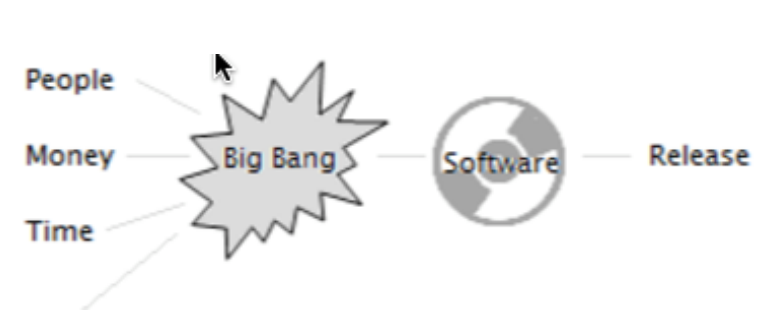
Comprises of focusing all the possible resources in software development and coding, with very little or no planning.
The requirements are understood and implemented as they come.
Any changes required may or may not need to revamp the complete software.
This model is ideal for small projects with one or two developers working together and is also useful for
academic or practice projects.
SDLC Agile
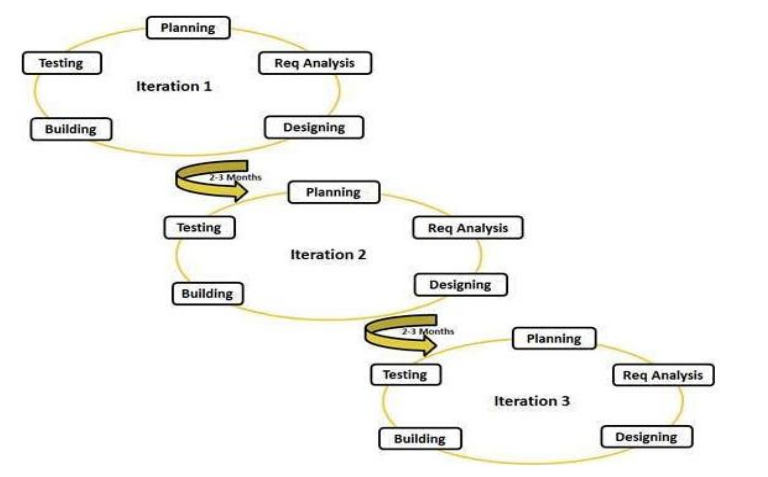
Agile SDLC model is a combination of iterative and incremental process models with focus on process adaptability and customer satisfaction by rapid delivery of working software product.
Agile Methods break the product into small incremental builds. These builds are provided in iterations.
Each iteration typically lasts from about one to three weeks. Every iteration involves cross functional teams working simultaneously on various areas like planning, requirements analysis, design, coding, unit testing, and acceptance testing.
At the end of the iteration a working product is displayed to the customer and important stakeholders.
SDLC RAD
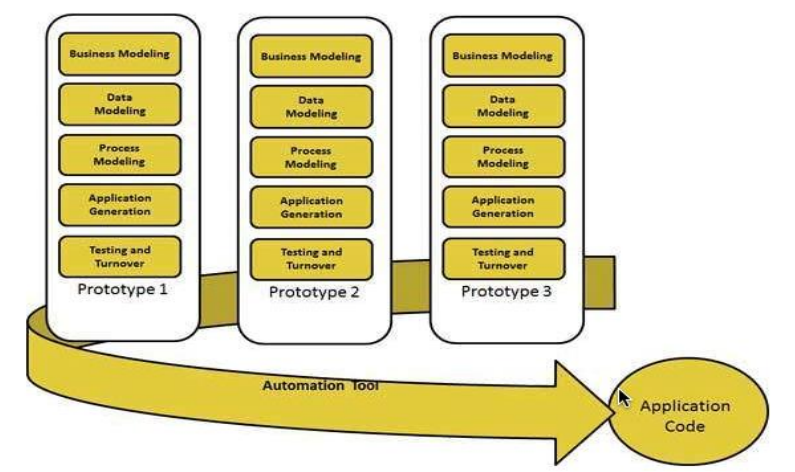
The RAD (Rapid Application Development) model is based on prototyping and iterative development with no specific planning involved.
The process of writing the software itself involves the planning required for developing the product.
Rapid Application development focuses on gathering customer requirements through workshops or focus groups, early testing of the prototypes by the customer using iterative concept, reuse of the existing prototypes (components), continuous integration and rapid delivery.

Activity – 1
+Select any 2 SDLC models discussed in our class today.
+Compare the 2 models and Discuss about the pros and cons. for both
+Duration – 25 mins
Handling Change
Most software needs to be constantly updated due to
the ever-changing dynamic in the business workConsider some of these best practices to help manage
the change with the intent of ensuring qualityBest Practices
Code Refactoring
Change Management
Configuration management
Version Control
Change Request Management
A clear Change request management process can help prevent conflicts and ensure that Change requests are handled appropriately
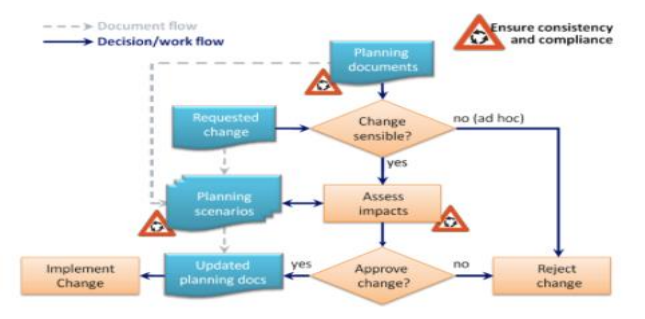
Version Control
Version control (also known as revision control or source control) is a category of processes and tools designed to keep track of multiple different versions of software, content, documents, websites and other information in development.
The purpose of version control is ensuring that content changes under development go as planned.
Version Control - GIT
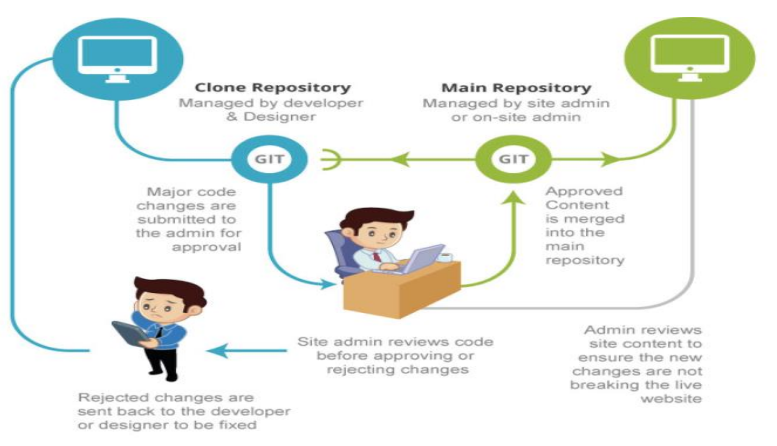
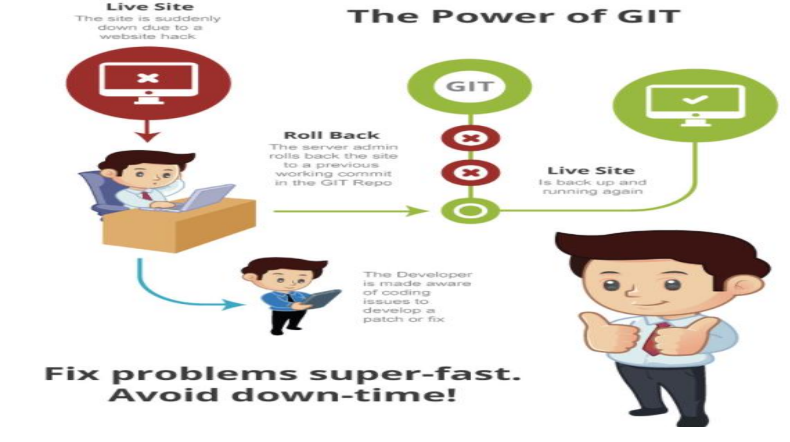
Summary:
In this chapter, we have covered
SDLC
7 Different SDLC Models
1.Waterfall, 2.V-Shaped Model, 3.Iterative,
4.Spiral, 5.Big Bang Model, 6.Agile and 7.RAD.
Handling change
Version Control
SDLC: Additional Reading Links: